

Therefore, electrophysiological thresholds were estimated with three audiometric frequencies and compared to the behaviorally measured aided and unaided thresholds. In this study, we measure the aided frequency-specific pure-tone hearing thresholds objectively by CAEP recordings with patients showing a sensorineural or mixed hearing loss. A stimulation artifact caused by the electromagnetic vibror has been observed only with the recording of auditory brainstem potentials and stimulation levels above 50 dB normalized hearing level (nHL) and is thus not relevant to threshold estimation with CAEPs. used the Baha softband (Cochlear Ltd., Australia) for the acoustical stimulation and showed a CAEP threshold of 20 dB above the individual hearing threshold. The behavioral threshold was reproduced with a difference of less than 10 dB hearing level (HL).
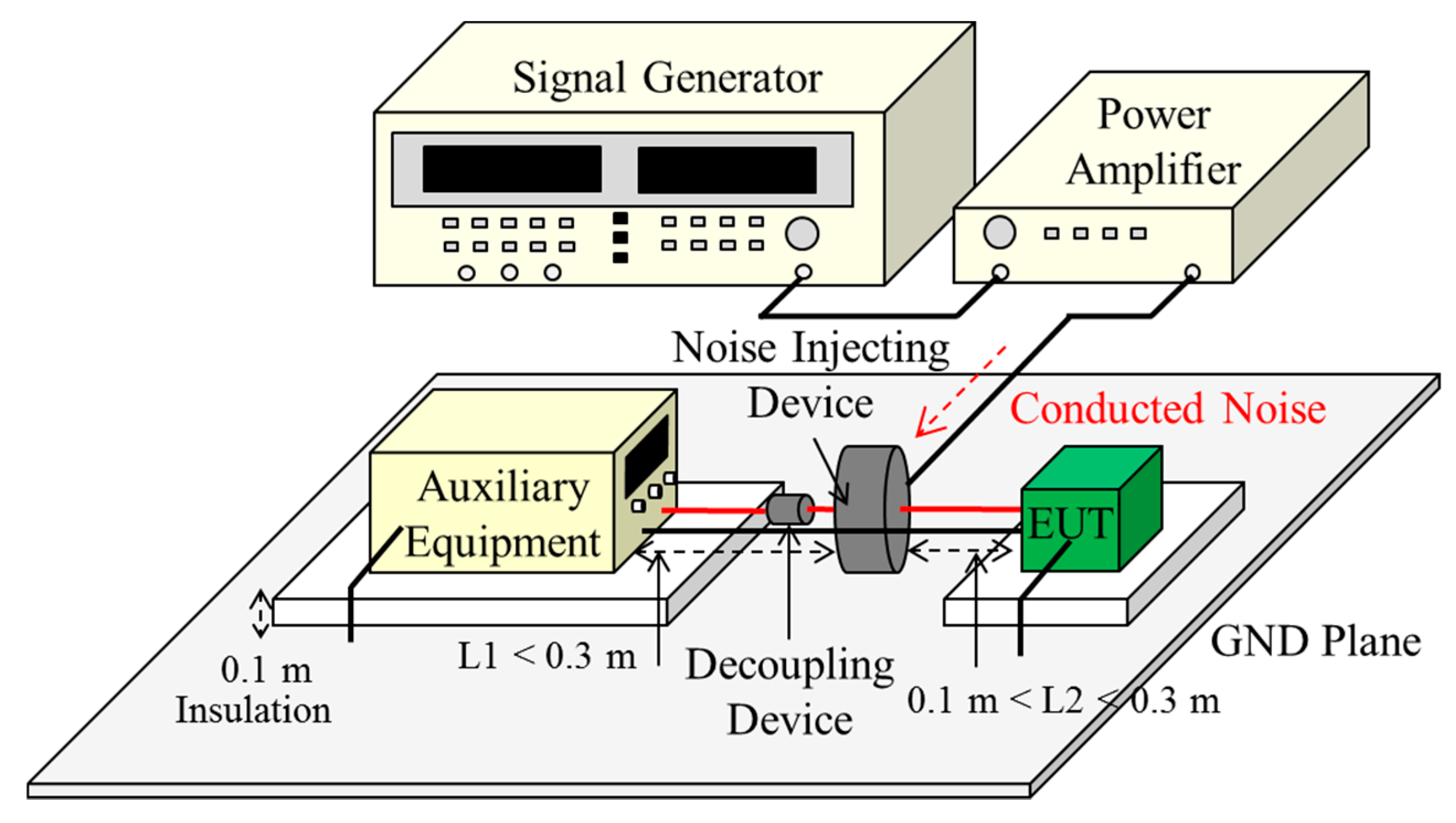
Measuring hearing thresholds with Baha users objectively, the recording of auditory evoked potentials using Baha as stimulator was recently shown in normal hearing adults. Therefore, the aided pure-tone audiogram serves as a control of the fitting. The sound processor needs to be fitted on the individual frequency-specific hearing loss. After osseointegration, a percutaneously connected electromechanical sound processor transmits the sound transcranially via bone conduction to the cochlea fluids. With the Baha, a titanium screw is implanted to the temporal bone. In this study, we apply the CAEP method to measure the hearing thresholds with adults using a Baha bone-anchored hearing system (Cochlear Ltd., Australia). ĬAEPs can also be reliably recorded in individuals when the acoustic stimulation is processed through a hearing aid. The resulting electrophysiological thresholds correlate with the behavioral measured frequency-specific pure-tone thresholds. As the amplitude and latency of the P1-N1-P2 waveform undergo significant maturation until the age of six years and the patients need to awake during the recording, this method is limited to juvenile and adult patients. Therefore, the lowest stimulation level where a P1-N1-P2 complex as a CAEP waveform with a latency of 50 to 175 ms can be discerned is usually defined as electrophysiological hearing threshold. Recording of cortical auditory evoked potentials (CAEPs) is the preferred method for the frequency-specific estimation of the hearing threshold.


Therefore, auditory evoked potentials (AEP) are applicable. With patients who are not able to provide thresholds behaviorally, such as young children or passively cooperative adults, objective methods are needed to estimate the hearing threshold. As subjective responses to the presented pure-tones are required, this method is not applicable only to passively cooperative patients. Introductionįrequency-specific estimation of pure-tone hearing thresholds is used as behavioral measure in clinical routine. Objective measurement of frequency-specific hearing thresholds with CAEPs is applicable to BAHS users. Increased thresholds were observed only with the 0.5 kHz Baha stimulation as compared to the pure-tone audiogram. For all stimulation frequencies, the frequency-specific electrophysiological and behavioral hearing thresholds measured with Baha stimulation were highly correlated and not different. Aided thresholds to tone bursts via Baha stimulation were obtained behaviorally and electrophysiologically using cortical auditory evoked potentials (CAEPs) and were compared to pure-tone thresholds using routine clinical audiometry. In a prospective study with ten adult Baha softband users, aided and unaided frequency-specific thresholds were estimated. With patients who are not able to provide thresholds behaviorally, such as young children, objective methods are required to estimate the unaided and aided hearing threshold and thus the success of the hearing system fitting. The amount of amplification provided by the hearing system is selected based on the individual’s sensorineural frequency-specific threshold. Patients suffering from conductive or mixed hearing loss may benefit from bone-conduction hearing systems (BAHS).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
